Are you thinking about upgrading your fiber optic network? Will your existing optical fiber infrastructure support the devices and services you plan to run? Could your organization benefit from having updated information about your fiber performance and inventory? If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, fiber characterization testing will help you gather the necessary data.
What is fiber characterization testing? Fiber characterization is a set of tests that delivers multiple, valuable measurements about the performance of your optical fiber infrastructure. As a result, you gather important insights that help determine if your existing network is suitable for intended upgrades, identify critical performance issues, and provide updated network performance and fiber inventory data.
In this article, we discuss the importance of fiber characterization, along with summarizing the types of tests typically performed as part of this service.

Above: A Certified Fiber Characterization Engineer (CFCE) performs essential fiber infrastructure tests using an OTDR.
Why is Fiber Characterization testing important?
As noted above, there are several reasons for establishing an updated fiber characterization report. The primary objective is to obtain current information and key metrics about the optical fiber infrastructure, including the fiber itself, connections, and performance characteristics.
In addition to a better understanding of the physical infrastructure, these tests are critical for determining the types of services and applications that can be supported by the network. For example, newer devices running higher bandwidth applications and utilizing advanced transmission approaches like wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) may require specific or newer types of fiber with improved specifications to run optimally. Also, fiber performance characteristics like attenuation, chromatic dispersion, and others play a role in the types of applications that can be deployed since specific types of fiber are designed to support different applications.
By performing these tests and having this information, a company can better assess the current network, along with anticipate future challenges that might arise if the infrastructure is not suitable to support intended upgrades or devices.
What is the result or potential drawbacks if fiber characterization testing is skipped? Simply put, skipping fiber characterization testing can have disastrous consequences costing a lot of time and money. As an example, a data center acquires 100G optical transceivers in the system for an estimated fiber link distance of 100m and has OM3 fiber installed. However, the actual link distance is 125m but it was not verified through fiber characterization testing. By skipping that step and link distance verification, the system will not perform as intended - OM3 fiber supports link distances up to 100m, but OM4 fiber is required for supporting link distances up to 150m. By not properly verifying the actual link distance in advance, the company might waste thousands or millions of dollars when acquiring the 100G optics for an infrastructure that will not support them.
For each fiber optic cable plant, it’s essential to test for continuity, polarity, and end-to-end insertion loss. From there, troubleshooting is vital to isolate and sectionalize problems and assign responsibility to resolve the issue as required.
Who benefits from Fiber Characterization testing?
Since fiber optics now serve as the primary technology medium for today’s communication networks, fiber characterization testing is essential for all sectors and entities that install, maintain, and rely on fiber optic communication networks. The sectors heavily invested in and utilizing fiber networks that require fiber characterization testing include telecom/ISP, data center, web/cloud, financial, government, energy, defense, and aerospace, just to name a few.
Who performs fiber characterization testing services?
Performing effective fiber characterization testing requires individuals with a high level of fiber knowledge, testing expertise, and the appropriate test devices. While some large enterprises that manage their own networks and infrastructure may have internal staff with the appropriate skill set and equipment to adequately perform the array of tests, in most instances the services are performed by 3rd party entities as part of their service portfolio.
Companies that construct fiber networks or turn-up systems like network engineering firms, fiber installers, and system integrators may offer all or a portion of the suite of tests depending on their service portfolio. Additionally, other types of entities that have the equipment and test optical fibers regularly, like M2 Optics which manufactures fiber network simulators and optical time delay solutions, also offer these services.
Individuals who perform these tests can obtain a special industry certification, the Certified Fiber Characterization Engineer (CFCE), which requires attending classes and passing related exams that provide the knowledge base necessary to perform the tests.
It should be noted that using an OTDR and other fiber characterization test devices to effectively obtain accurate and precise results requires a skilled engineer or technician with extensive expertise in using these devices along with a deep understanding of optical fibers and their characteristics.
Lastly, many entities relying on fiber networks will often prefer a 3rd party to provide fiber characterization testing that is independent of the company providing or managing the fiber. Utilizing an independent testing service may be a compliance measure, but in other cases, an entity may offer competitive services to the entity that owns the fiber and therefore prefers an independent, unbiased evaluation.
Types of Fiber Characterization Tests
Since fiber characterization is comprised of suite tests, we’ll now quickly highlight the types of tests that are performed. It’s important to note that not all companies offer the exact same number or types of tests as part of their service portfolio since some tests require different levels of knowledge or access to specific test devices and features, but generally, there are a set of “standard” tests along with a set of “advanced” tests. A few of the tests may be included in one set or the other, depending on the service provider's offering. Additionally, some service providers may provide hourly service rates that include the complete set of tests, while others may have a different rate for standard versus advanced tests.
Standard Fiber Characterization Tests
Some of the tests that typically fall under the category of standard or base testing packages include:
- OTDR: Using an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR), the physical integrity, continuity, and distance of a fiber are measured accurately. An OTDR works by transmitting an optical pulse across a fiber, then evaluating backscattered reflections returning to the device created by reflective events in the fiber that include splices, connection points, fiber mismatches, or the endpoint of the fiber.
- Insertion Loss & Return Loss: These two important measurements are used to further evaluate loss and reflection events when analyzing system and link loss budgets, evaluating connections, and more.
- Visual Connector Inspection: This test identifies dirty or damaged connectors that negatively impact performance and contribute to high signal loss. Using an inspection scope, dirty or damaged connector end faces will visually show the issue, which then guides network teams to take the appropriate cleaning or replacement measures to resolve the issue.
- Fiber Link Latency: Taking into account the relationship between a fiber’s Index of Refraction (IOR), physical length, the speed of light, and signal wavelength, this test determines the time delay incurred when transmitting a light signal over the length of the optical fiber. While this test is not always included in the standard set of tests, it is essential for latency-driven systems and applications where system timing is of critical importance.
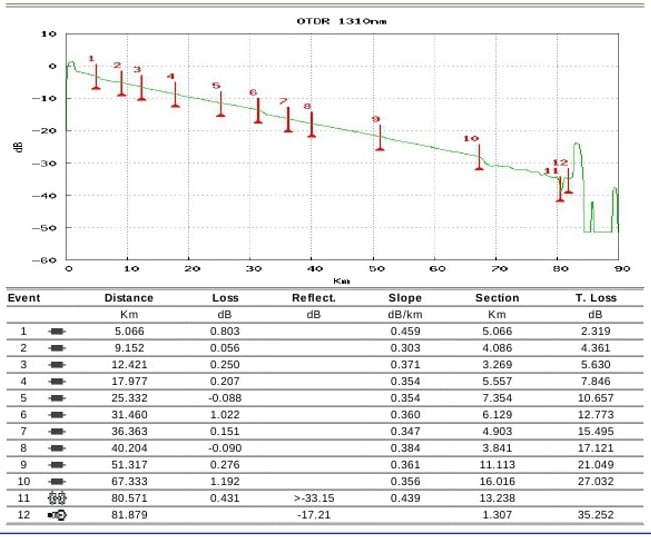
Above: Example of an OTDR trace displaying numerous signal attenuation/loss events in a fiber span.
Advanced Fiber Characterization Tests
While most entities will require the standard set of tests at a minimum, some require a more advanced set of tests to also be conducted based on planned or targeted system services and applications. These advanced tests can include:
- Bit-Error-Rate (BER) for 10G: BER is an important test at the data and packet level that determines the average number of incorrectly transmitted and received bits. While BER is another technical topic in itself, this is a key factor in the quality of system performance, so measuring and then taking steps to minimize bit error rates is an important goal.
- Bit-Error-Rate (BER) for 40G and 100G: Similar to BER testing for 10G systems, these tests are utilized for higher bandwidth systems like 40G and 100G currently deployed in today’s major data centers.
- Chromatic Dispersion (CD): Chromatic dispersion occurs as different spectral components of light arrive at the destination at different times since they travel at different speeds. CD characteristics are detrimental to light transmission, especially as fiber distances increase, so testing for this performance characteristic and taking appropriate measures if needed (ex: utilizing dispersion compensating fibers) is important.
- Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD): PMD occurs when two polarizations of light normally traveling at the same speed arrive to the destination at different times. As this too can negatively affect performance, testing for it is necessary for some systems applications more than others. PMD is one of the more difficult characteristics of light transmission to compensate for, but there are polarization-maintaining fibers and components specifically designed for installation into applications where this must be addressed.
- Spectral Attenuation (SA): SA is the measurement of attenuation (signal loss) dependent upon the wavelength being transmitted. This type of test is more prevalent in systems running Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) applications like CWDM and DWDM systems, where multiple wavelengths are combined onto a signal fiber for transmission purposes.
M2 Optics - Your Fiber Characterization Testing Partner
With the continued growth of fiber optic networks and advanced network devices, fiber characterization testing will become even more critical for ensuring systems deliver the expected performance capabilities. Partnering with an independent fiber characterization service provider like M2 Optics provides the necessary expertise and testing equipment and can help your organization by:
- Delivering accurate fiber network infrastructure performance results and data
- Saving you time and money - no requirement to hire and train staff or purchase expensive test gear
- Serving as an independent entity generating unbiased, trustworthy results
M2’s fiber characterization staff has experience testing a wide range of optical fiber types in a variety of network environments while maintaining extensive knowledge and fiber testing certifications like the CFCE and others including Corning®, BICSI®, and FOA/CFOT®.
Since testing needs differ by project and network, M2 Optics offers a customized testing package approach and will schedule a brief consultation to learn more about your requirements. Whether performing a single type of test or the entire portfolio, our goal is to help you achieve your goals and objectives in the most efficient manner.
Contact M2 Optics to learn more about our Fiber Characterization Testing Services or to schedule a consultation.