With the rapid evolution of technology, high-speed communications systems are essential for enabling telecom service providers to deliver large amounts of content around the world. The demand for faster speeds and more bandwidth is rising and optical fiber cables, which allow for the transfer of data using light signals, serve as the primary medium in these networks.
Since both the devices and the cable infrastructure used to make the connections are critical, it fiber optic testing must be conducted at many application levels to ensure optimal performance. In addition, testing maximizes this technology’s capabilities significantly by helping to troubleshoot, identify, and fixing issues that can be detrimental to the network performance.
As fiber optic testing is performed during different phases and applications, it raises some general and common questions from those interested in learning more about the topic. In this article, you can find answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about fiber optic testing. Let’s explore further.
4 Top FAQs about Fiber Optic Testing Answered
1. What is fiber optic testing?
Fiber optic testing is the verification of the performance and the integrity of fiber optic devices, signal transmission, cables, and/or overall networks. As fiber networks are expanding in size and complexity, testing is required at both the physical layer and the data layer to ensure that the relevant industry standards are met, and the system is performing optimally.
As the demands for greater performance requirements are increasing, issues that arise can range from being minor to very serious complete service outages. Therefore, accurate and timely testing is needed at all network levels and phases to verify the continued readiness of the overall system.
Effective fiber optic testing results in several key, high-level benefits:
- Devices perform at their maximum level.
- Overall, system performance is enhanced.
- Issues are detected and addressed faster, increasing reliability and uptime.
2. What are some examples of fiber optic testing standards?
To ensure consistency, national and international standards have been developed over the years that companies and individuals must strive to adhere to.
For different testing categories, there are bodies that serve to develop sets of standards. While there are numerous bodies that exist, a few of the most recognized include:
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
This global standards organization provides the technical framework for quality optical fiber infrastructure and certifies that the installations, devices, and systems work as per the defined cabling standards. Adherence to these standards ensures that the fiber optic interconnecting devices and passive components are safe and reliable.
Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
This association creates standards and technical documents to ensure quality and achieve functionalities of optical fiber cabling components. These standards are established as per the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) requirements that support telecommunications cabling and infrastructure.
Other Standards
In addition to those mentioned above, other important standards within the fiber optic communications industry include:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Telcordia (Bellcore) Testing Standards
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
3. What are some example of common fiber optic testing equipment?
Fiber optic testing equipment includes instruments designed to troubleshoot and analyze fiber optic cables, systems, and device performance. Since test equipment is used for laboratory, manufacturing, and field applications, for the purposes of this article, we have specified some of the common field test equipment utilized frequently by network technicians. Some examples of the most common test devices include:
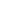
Fiber Optic Power Meters (OPM)
The optical power meter is an essential instrument designed to measure absolute optical power transmitted through an optical fiber. While a fairly basic device in terms of the results generated, they are highly useful for quickly identifying excessive signal loss, denoting an issue exists somewhere in the fiber cable.
Shown: Handheld Optical Power Meter
Fiber Optic Light Source (OLS)
Fiber optic light sources are instruments used in combination with fiber optic power meters to determine signal loss levels through fibers. For instances where a source signal does not exist (ex: dark fiber) to test or a different wavelength is preferred, a light source provides the necessary signal to perform the test using a power meter at the other end of the fiber.
Fiber Optic Multimeter
A fiber optic multimeter provides more testing capabilities than other devices like a power meter, with features that allow for measuring optical loss, return loss, length, and power levels. In addition, there is generally a slightly improved user interface that a technician can use to easily select the desired testing function, change setting parameters, and more.
Visual Fault Locator (VFL)
A fiber visual fault locator is used for detecting any bends or breaks in an optical fiber. It is often manufactured as a pen-type device and comes with a universal adapter. It operates by sending a visible light signal through the fiber and if there are any breaks or weak points in the fiber, the light will be visible to the user at those points, identifying the locations of the issues.
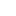
Optical Fiber Identifier (OFI)
This instrument is another device designed for fiber optic network maintenance. It can detect the presence or absence of data traffic on fibers and the direction of the data traffic. This helps the user to identify specific fibers during testing, maintenance, and connectivity tasks.
Shown: Optical Fiber Identifier with integrated VFL
4. What are a few of the different fiber testing applications?
Fiber optic testing does not apply to a single instance but rather occurs in many different application areas. Equipment manufacturers test devices in labs during R&D, service providers, test various equipment to determine the best fit for their network needs, and field technicians test and troubleshoot networks after deployment to maintain network performance and resolve issues that arise. Let’s take a brief look at a few of these applications.
R&D and Manufacturing
At the device and component level, network equipment manufacturers perform numerous instances of testing during proof-of-concept, research and development, and certification stages. Not only do testing procedures ensure that devices they design and manufacturer will meet the intended performance specifications, but they also must test in accordance with industry standards and a variety of potential scenarios under which their customers may use the devices.
System / Device Verification & Certification
While devices and components are designed and tested in labs by the manufacturers, telecom service providers and other entities that install and maintain network equipment need to ensure the devices are the ideal match for their unique network. While two manufacturers may produce similar devices, even minor changes in performance specifications could produce significantly different results depending on the desired setup configuration and network requirements. Thus, service providers and network integrators will perform their own testing in an effort to select the equipment best suited to their needs.
Additionally, different types and brands of optical fiber will produce different results. So in a similar manner to testing devices and network gear, service providers will also test the performance of different optical fibers to determine which type of fiber is preferred for the cables in their network.
For both device and optical fiber certification testing, using a customized fiber network simulator will produce performance results that accurately replicate the field network, so this has become a best practice across the industry.
Installation and System Turn-up
After the network infrastructure and equipment has been selected and acquired, network operators must then install and set up the system. Testing occurs at multiple phases of this process, from testing the cable infrastructure itself through fine-tuning equipment settings after devices have been connected.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Once a fiber optic network has been installed and is operating or in service, the network must be monitored continuously for issues that can arise in both the physical or data layers of the network.
We have all experienced intermittent internet connectivity, some have experienced complete outages, and in general, a variety of issues can arise at any time in a network. Simply put, maintaining a fiber optic network is not easy, so operators employ service teams for both troubleshooting and resolving issues when they arise, as well as install monitoring equipment in an attempt to identify and localize issues as quickly as possible in an effort to maintain maximum uptime and performance.
An example of equipment for monitoring a network is remote fiber monitoring systems. These devices can be easily installed within the network environment and notify service teams in real-time when a physical fiber issue like a break or tampering attempt occurs.
Learn More - Fiber Optic Testing
Whether in the laboratory or the field, performing effective fiber optic testing is critical for ensuring all communication devices and networks perform at a maximum level.
M2 Optics supports entities designing, manufacturing, installing, and maintaining fiber optic systems with their testing efforts by offer a portfolio of customized, efficient solutions proven to deliver maximum value. Contact our team of fiber experts today to learn more about:
- Fiber Network Simulation Solutions - Packaged Optical Fibers
- Fiber Monitoring Systems
- Handheld Test Devices - MPO Power Meters, Optical Fiber Identifiers, and more